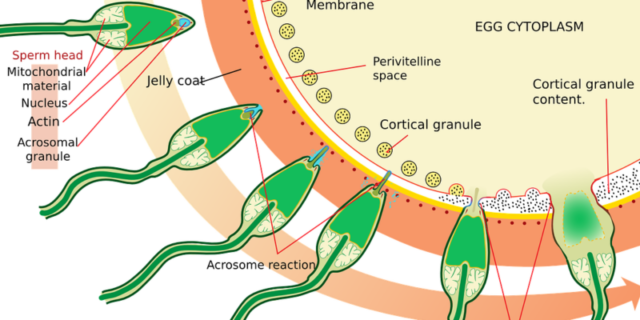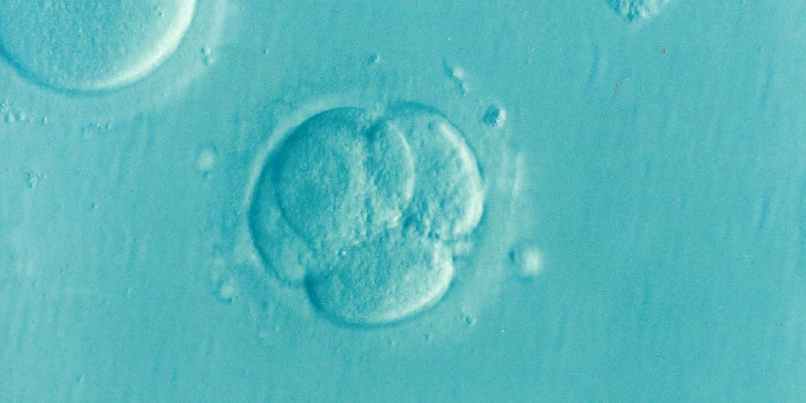
So-called IVF or In Vitro Fertilization is the process of fertilization where an egg is fertilized by sperm outside the body. In Vitro, by the way, means “in glass.”
The treatment also monitors and stimulates (usually with Fertility Medication) a woman’s ovulatory process. When eggs have developed one removes (extracts) an egg (or more eggs), the so-called ovum or ova from the woman’s ovaries, and let sperm fertilize it (insemination) in a special liquid in a laboratory. It’s a manual process.

After the fertilized egg starts embryo culture for two to six days, the embryo (zygote or fertilized ovum) is implanted in the woman’s uterus (or another woman’s uterus), with the goal of beginning a successful pregnancy.
The most common reasons to apply IVF are blocked, damaged or removed fallopian tubes, decreased sperm count or sperm motility, ovulation disorders, premature ovarian failure, uterine fibroids, genetic disorders, and unexplained infertility.
The success rate depends on a variety of factors including reproductive history, maternal age, the cause of infertility, and lifestyle factors. Mind that pregnancy rates are not the same as birth rates, which means that it’s certainly not always the case that the treatment will result in childbirth.
Usually most women can resume normal activities the day after implantation, but some light side effects may be the case, such as passing a small amount of fluid, mild cramping or bloating, constipation, and breast tenderness.
Heavier side effects that need medical attention are heavy vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, blood in the urine or fever, to name a few indications.