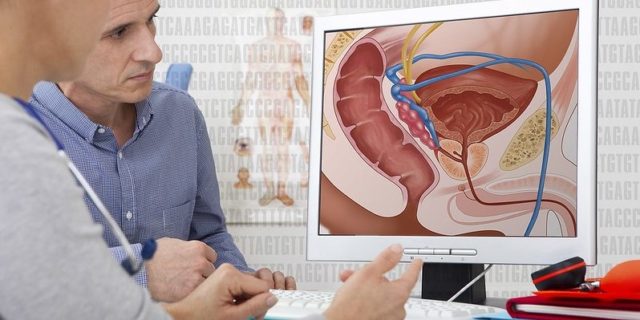
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection that affects parts of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a Bladder Infection (Cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it’s called a Kidney Infection or Pyelonephritis.

The typical symptoms of a lower UTI include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. UTI symptoms have a strong resemblance with the symptoms of an Enlarged Prostate.
The symptoms of a Kidney Infection include fever and flank/side pains often coming together with the symptoms of a lower UTI as mentioned above. Sometimes urine may appear bloody. In both very old and very young people the symptoms may be vague or non-specific.
The most common cause of infection is the Escherichia Coli bacteria, though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history.
Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, an UTI is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection (STI). If a Kidney Infection occurs, it is usually after a bladder infection, but it may also result from a blood-borne infection.
Urinary Tract Infections are more common in women than men and are usually treated with antibiotics.