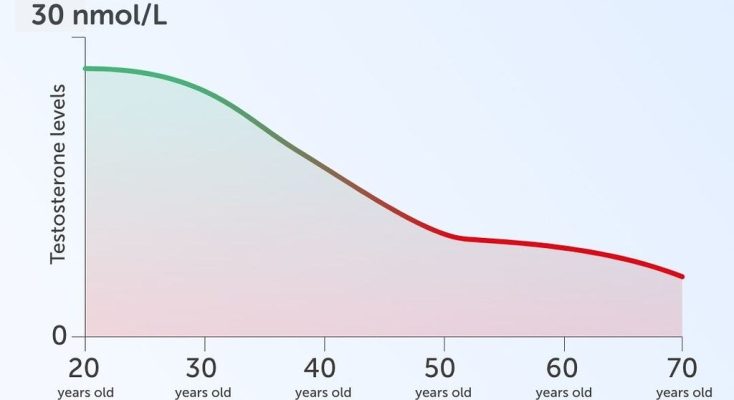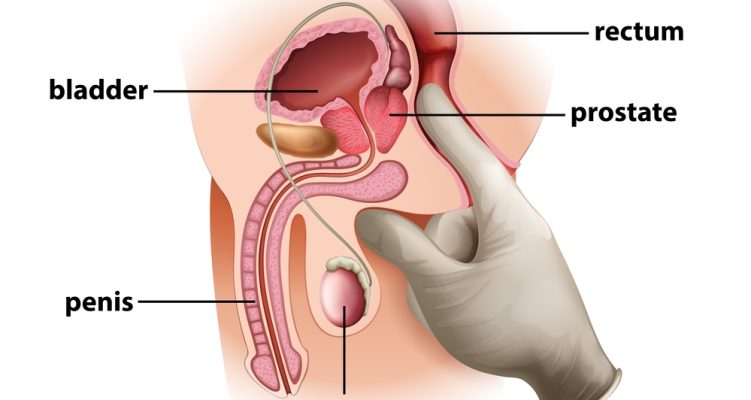
In humans, the prostate is a small gland of the male reproductive system that primarily produces and releases (secretes or discharges) certain substances.

The prostate gland — being surrounded by connective tissue — is usually about the size of a walnut, weighs about 30 grams, and it’s found below the bladder, in front of the rectum, while it partly surrounds the tube (urethra) in the penis that leads pee from the bladder.
The prostate is a multi-functional organ that has a variety of aims, such as filtering, regulating, arousal, secretion, nerve signaling, and pumping.
An important function of the prostate is to secrete a fluid during ejaculation (which through its ducts flow into the urethra), which is milky or white in aspect, and in humans usually contains about 30% of the volume of semen along with spermatozoa and so-called seminal vesicle fluid.
Prostatic fluid is expelled in the first part of ejaculation by muscle cells in the prostate that contract and press the fluid that has been stored in the prostate out into the urethra. This is also the moment that most of the sperm and other seminal fluids pass along the prostate, so that prostate fluids optimally mix with the sperm cells.
In addition, the prostate secretes a crucial enzyme that plays a role in sexual arousal and libido, together with zinc, citric acid, and fructose which help nourish sperm cells and lubricate the urethra.

Another important function of the prostate is to filter and remove toxins for protection of sperm, making the latter of better quality. Nevertheless, these toxins can become a cause of prostate illnesses if they only accumulate and are not flushed properly.
The prostate also has some muscles that help excrete semen during ejaculation, giving the prostate a kind of pump function. Furthermore, it’s also a valve that regulates urination or ejaculation flow.
Although not part of the prostate, around it one finds important blood vessels and nerves that aid in getting an erection. Certain prostate diseases and/or the treatments for those diseases may damage these blood vessels and nerves which can result in erectile dysfunction (ED).
The prostate is also considered a sexual pleasure spot, usually called the male G-Spot (or P-Spot). The latter is typically manipulated by carrying out an internal or external Prostate Massage.
Nevertheless, Prostate Massage can also be part of a rectal examination (DRE), which is given to men by an urologist to look for signs of prostate cancer, but also to obtain a prostatic secretion sample for microbiological research, for instance to diagnose prostatitis.