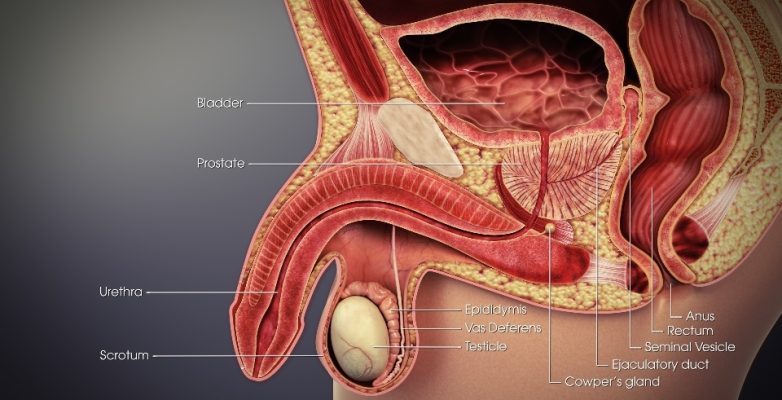
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as prostate gland enlargement, is a prevalent condition that primarily affects men over the age of 50. Although it isn’t life-threatening, it can significantly impact quality of life, leading to discomfort and inconvenience.
Understanding BPH is crucial for those directly affected and their families and caregivers. This article aims to understand BPH by thoroughly understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. By raising awareness and promoting informed discussions, we can empower men to seek timely medical advice and manage this condition effectively, ensuring a better quality of life.
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
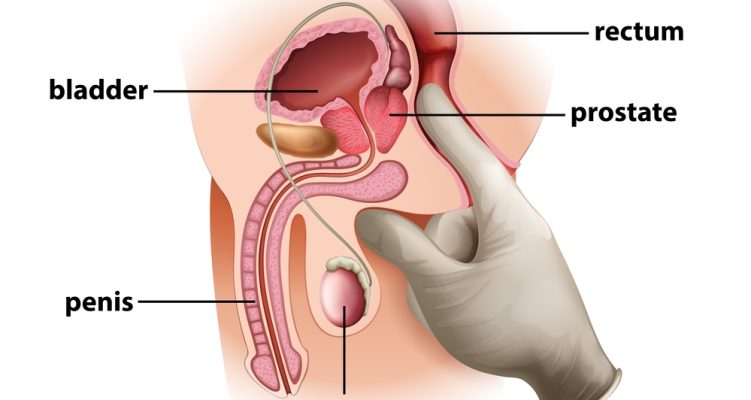
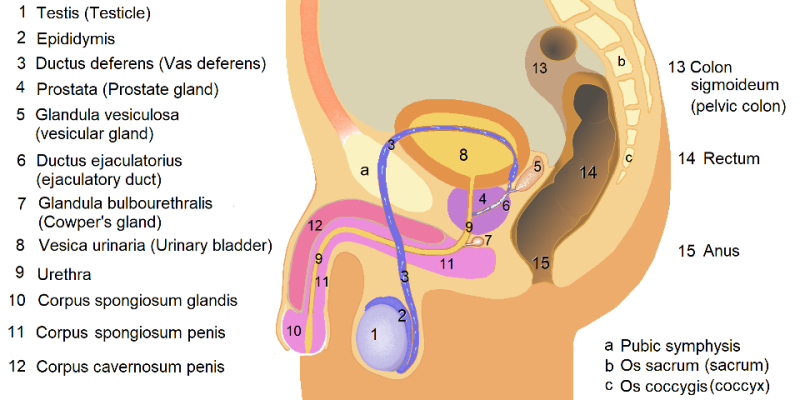
BPH is the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, a walnut-sized gland in men that encircles the urethra and plays a pivotal role in the male reproductive system. This enlargement can lead to uncomfortable urinary symptoms, and if it’s left untreated, more severe complications can occur.
Usually, the treatment would depend on the severity of symptoms, many patients take Tamsulosin since it’s a widely used medication. Thanks to Tamsulosin Uses and recovery for the prostate, it makes a crucial medicine to manage BPH. It helps relax prostate and bladder muscles, easing urination and improving urinary flow and frequency symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
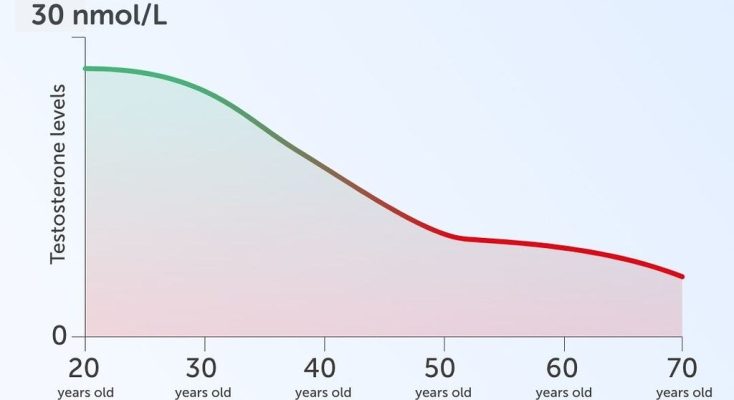
The exact cause of this condition remains unclear, but it’s primarily linked to aging and changes in the balance of sex hormones. Risk factors include age (most common in men over 50), family history, lifestyle choices like diet and exercise, and other health conditions such as obesity and heart disease.
Symptoms of BPH
Symptoms of BPH would vary, but they often include the following:
- Difficulty starting urination
- A weak urine stream
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Increased frequency of urination at night (nocturia)
- Inability to empty the bladder
These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Treatment Options
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in older men without a known cure, but it can be effectively managed. Treatment strategies include lifestyle changes, such as adjusting fluid intake, exercising regularly, and taking medication.
While Tamsulosin significantly alleviates BPH symptoms, it does not cure the condition. In cases where medication is insufficient, surgical options may be considered. Effective management of BPH through lifestyle adjustments, medications, and possibly surgery can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications are crucial in managing BPH, reducing symptoms, and improving quality of life. Regular exercise is particularly beneficial, as it can help maintain a healthy prostate and overall body health.
A balanced and healthy diet is equally important, as it can influence prostate health and potentially reduce symptoms. Moreover, for individuals with BPH, limiting fluid intake in the evening can be a practical approach to decrease the frequency of nocturia, a common and often disruptive symptom of BPH. Adhering to these lifestyle changes can significantly aid in managing the symptoms associated with BPH, enhancing daily comfort and well-being.
Complications and Prevention
Indeed, as mentioned above, BPH is a common condition. However, being aware of its potential complications and adherence to prevention strategies, including regular medical check-ups and lifestyle modifications, are vital in mitigating risks and ensuring a better health outcome. So, if you have BPH, be sure to keep the following complications and preventions in mind:
Complications of Untreated BPH
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): The inability to fully empty the bladder can create a breeding ground for bacteria, increasing the risk of UTIs. These infections can cause discomfort, pain, and complications if not treated promptly.
- Bladder Stones: These are small mineral masses that form in the bladder. The stagnation of urine because of BPH can lead to the formation of these stones, causing additional urinary symptoms, discomfort, and even blockages.
- Kidney Damage: The most severe complication, prolonged urinary retention, can cause pressure back-up into the kidneys, leading to kidney damage. This condition, known as hydronephrosis, requires immediate medical attention.
Prevention Strategies
The risk of these complications can be significantly reduced through early detection and proper management of BPH.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups, including prostate exams, are crucial, especially for men over the age of 50 or those with risk factors such as a family history of prostate issues. Early detection of prostate enlargement can lead to timely intervention.
- Lifestyle Modifications: As mentioned earlier, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and controlled fluid intake can help manage BPH symptoms and may slow their progression.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Being vigilant about changes in urinary habits and symptoms is vital. Prompt consultation with a healthcare provider at the onset of symptoms can prevent complications.
- Medication Compliance: For those prescribed medications like Tamsulosin, adherence to the treatment plan is essential to manage the condition effectively and prevent complications.
Final Thoughts
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is a condition that, though common, can profoundly impact a man’s life as he ages. It is essential to recognize the importance of early detection and treatment to prevent complications and maintain a good quality of life.
Stay informed about BPH, and take proactive steps in consultation with your healthcare providers to manage the condition effectively. As research continues and treatment options evolve, there is renewed hope for those living with BPH. With the right approach, BPH can be a manageable part of life, allowing men to continue enjoying their everyday activities with minimal disruption.